QR code use in Asia and the key opportunities for marketers

QR codes, while associated with the information age, are actually nothing new. Quick Response code technology was initially developed as far back as 1994 as a means for Japanese auto manufacturers to keep track of the numerous different components on the production line, and is itself an extension of the barcode technology that has been around since the 1970s.
However, the advent of smartphone technology and the growing ubiquity of extremely powerful hand-held digital devices have brought QR codes off the factory floor and into daily life. Today’s social media users will be familiar with QR codes as a quick method of registering for special offers and competitions or for following accounts. But the future of QR codes is far more expansive than this. In fact, this future is already here in many global markets.
A significant shift in technological capability
Perhaps it is a little unfair to describe these codes as merely an extension of the barcodes we see in stores and on retail products. While both concepts represent a means of storing and presenting information, QR codes are far more sophisticated than their predecessors. While barcodes link with digital inventories to provide stock and pricing data, they are simply coded representations of a numeric value. QR codes can hold and present data on a much grander scale, including everything from image and text files to URL links and geo-positioning coordinates.
Even more exciting is the scanning potential of barcodes. You don’t need an unwieldy barcode scanner to access a QR code — you simply need a smartphone. And smartphone technology has already achieved high levels of penetration within the general public.
Asia still leads the way
It is telling that QR code technology comes to us from the Asian nation of Japan. When it comes to widespread usage, Asia is streets ahead of much of the rest of the world. While this does mean that the US is lagging behind somewhat in the adoption of this new and exciting technology, it also means that marketers have a wealth of untapped opportunity right at their fingertips — and a broad range of use cases to draw inspiration from.
Let’s take a look at these use cases, examining how marketers can benefit from this technology.
The growing influence of QR codes in the Asian market
Data from GlobalWebIndex shows that Asia is leading the world when it comes to QR adoption. Specifically:
- 15% of the population of the Asia-Pacific region are “QR code users.” A QR code user is defined as “someone who has used a QR code provided by a company or brand in the last month.”
- Latin America is not far behind, with 13% of the population classed as QR code users.
- Europe and the Middle East are tied in third place at 10%.
- North America lags behind at 8%, although adoption in the United States is gathering pace.
However, while the data is clear, the reality on the ground is even more remarkable. Resources from the Asia-Pacific region include datasets from markets such as Australia and New Zealand, where QR code usage is less widespread. When we look at East Asian markets like China in isolation, the results are quite astounding.
In 2018, research showed that 70% of the population were “regularly using QR codes to make payments.” In total, it was estimated that mobile app payments — the majority of which are handled via QR code — hit 277.39 trillion yuan ($42.4 trillion). By 2019, this had jumped to 347.11 trillion yuan ($53.1 trillion), more than double the value of four years earlier and more than triple the value of five years earlier.
As of June 2020, it was estimated that around 801.7 million people used a mobile payment app to complete a transaction in China, up from 765 million in March 2020. This continues to be a growing market, despite its seemingly total dominance in locations such as China.
While the US and other Western markets have seen a slow evolution from cash-dominated economies to in-store card payments and contactless transactions, China’s development has been more direct. Over the last decade, China has moved from a largely cash-only situation — with bank card usage reserved for cash withdrawals and big-ticket purchases — to the widespread adoption of digital wallets and smartphone app-based transactions. QR codes have facilitated this cultural shift and have seen China surge ahead of many of its rival global markets.
The common use cases: How is QR code technology being used in Asia?
Source: https://www.theasianbanker.com/updates-and-articles/qr-code-payment-system,-a-game-changer
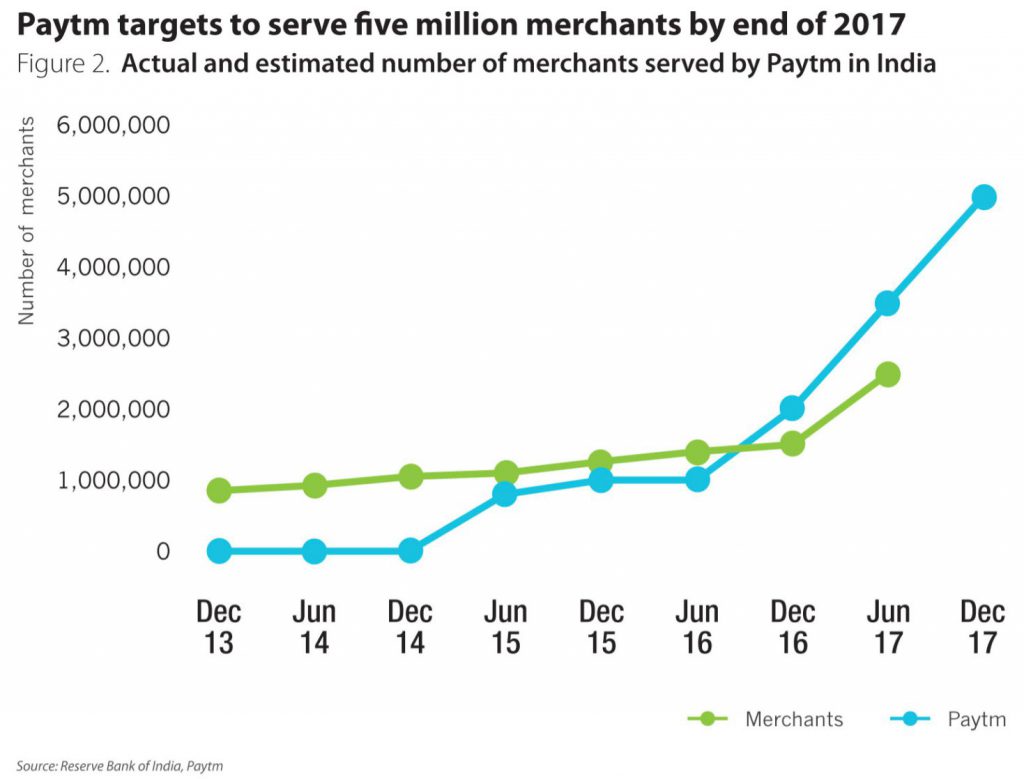
Increasing usage figures for QR code-based payment provider Paytm in India.

Source: https://news.cgtn.com/news/7759444e34637a6333566d54/index.html
There are many different potential use cases for QR code technology, and Asia is leading the way in terms of possibility and capability for QR. Here are some of the most interesting use cases for QR codes — all of which are currently being deployed in markets across Asia and elsewhere.
Mobile transactions
As discussed above, mobile transactions offer the most obvious use case for QR codes in Asia. QR codes provide a secure link between mobile wallet technology and real-world actions. This is why QR code payment options are found in physical stores right across many Asian markets.
Staying informed
Deploying QR codes on things such as signs in the workplace or within brochures and other information resources helps users access additional information and support on key topics. This saves a lot of space, allowing designers to get their message across while still providing high levels of information for those who need to use it.
ID authentication
QR codes can link with biometric data to authenticate IDs and other important documentation. This makes the technology potentially very useful indeed in securing sensitive areas of businesses and other organizations, as well as easing the strain placed on human reception teams. Examples of the deployment of this technology include requiring scannable QR codes in staff-only areas of a business’s premises or providing tiered access to different areas of a company. This can be paired with biometric information for additional verification.
Using social media
Individuals can use QR codes to quickly add one another on social media or to join groups of like-minded people on social platforms. Again, the codes offer a secure and efficient way to carry out quick actions, enabling faster, safer engagement. In Asia, social platforms such as WeChat have embraced QR codes completely, using them for a range of purposes, from connecting with official accounts to making subscription payments.
Verifying and understanding products
Codes can be deployed on products to provide more information on the ingredients or use cases for a product and to allow customers to verify the product before they make a purchase.
App downloads and linking products with app technology
Let’s say a user hears about a new app and then decides to download and utilize this app. If they have to search for the software via a download platform, or if they need to head elsewhere to find the app, it’s just adding unnecessary links to the chain. The user may decide to give up halfway through the process. QR codes permit swift downloads with minimum effort. Consumers can also use QR codes to identify verified products.
Augmented experience of advertising media
Advertisers can provide a far richer experience to the general public when they use QR codes. By scanning a code on a print ad or another physical medium, the user can access all manner of other data and capability. This allows companies to engage their users on a far more profound level.
Promotions and discounts
Consumers can scan QR codes to connect with promotional campaigns or discounts. This gives customers the opportunity to save money on items they love, while businesses have the chance to foster ongoing engagement.
Software login
This is a quick, easy, and secure way to log into a piece of software. The user scans the QR code to get verified and then accesses the software with no delay or point of friction. This also integrates with hardware in many examples — for instance, using QR codes on public bicycles. The app reads the QR code, and the app sends a signal to the bike to unlock, ready for use.

Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lime_(transportation_company)
Combating coronavirus
QR codes have been used effectively to track and combat coronavirus. Users can have their testing data and other biometric information linked to a profile, which is then accessed with a QR code. If the user has symptoms or has tested positive, they may not be permitted entry to a certain location. Also, outbreaks of COVID can be traced back to specific locations, enabling at-risk individuals to get tested quickly and effectively.
Culture and traditions unique to the region
While the above use cases do provide marketers with a degree of inspiration, there are some key points of difference between domestic and Asian markets that business owners need to be aware of.
Widespread consumer knowledge
QR codes are being rolled out rapidly across China and other Asian markets, and this is being driven by widespread consumer knowledge and understanding. This shift is also happening in the US, but at a much slower rate — thanks in part to a lower level of consumer knowledge.
A lack of competing structures
Contactless payment is already possible in the United States, providing a means of payment that is almost as quick and efficient as scanning a QR code. In many global markets, these competing structures don’t exist.
Less stringent data protection laws in the United States
When QR codes are used for ID verification and other similar purposes in the United States, they may come into contact with areas of data protection and privacy legislation. Business owners need to work hard to make sure they are on the right side of regulations.
A warmer reception for digital wallets in Asian markets
Digital wallets such as Alipay and WeChat already dominate Asian markets, with other disruptors and competitors also developing their market share. This has made it easier to deploy QR codes across Asian markets, whereas implementation in the US will require additional steps to reach maturation.
Lingering distrust of QR codes from some parties in the United States
While QR codes are becoming more widely deployed in the United States, there are some that remain concerned about their security. Scanning QR codes has become a daily — or even an hourly — reality for consumers in China and other Asian markets and has been adopted wholeheartedly. It may take more of a public relations effort from QR code champions to win over some sections of the American public.
QR codes and the coronavirus
QR codes can be easily edited and modified and then tracked, allowing for swift customization and deployment. Large-scale projects, like the unprecedented global fight against COVID-19, are ideal forums for QR codes, which provide information and verification as well as crucial tracing capability.
The Chinese government has put its weight behind the technology. Not only has it opted to use QR codes to keep on top of the domestic spread of the virus, but it is also leading calls for a global COVID QR code to assist economic recovery on a worldwide scale.
While it is unlikely that wholesale global adoption will take place in the near future, studies have shown that QR code technology, deployed alongside tracking apps, can make a real difference. In April 2020, Oxford University published a study showing that even if only 56% of the total population of a country were using the tracking technology, it would have a significant impact on slowing the spread of the pandemic.
The accelerating rise of QR codes
As we look forward to a post-COVID world, it seems likely that QR codes will be here to stay. All the figures point to a continuing rise for this tech, and the fact that the vast majority of smartphones now include built-in QR code scanners shows us that the capability is already there. In fact, marketers across most industry verticals, from hotels and social media influencers through to B2B and B2C companies, are already intrigued by the potential of these codes.
We have already seen how effective these pieces of technology are in markets across Asia. Now it’s time for other global markets — such as the US — to join the forefront of this tech movement.
To learn more about getting the most out of QR codes, either in the US or the Asia-Pacific region, reach out to our team today.
About Principle
Principle helps businesses of all sizes make better decisions through data. For the better part of a decade, we have helped global brands and Fortune 500 companies turn data into intelligence and actionable insights they can use in digital marketing.
Our team of 100 employees includes experts across Analytics, Paid Marketing, SEO, and Data Visualization. We offer actionable and measurable data analytics strategies, SEO, and campaign management services that deliver the digital transformation your business needs to outperform the competition.
We recruit independent professionals who have their own personality, an established way of life, a unique skill, and can share our philosophy. With such colleagues, we believe that individuals and companies will grow together and achieve great quality and result in an unseen business world.
To learn more about digital marketing and advertising in Japan or elsewhere in the Asia-Pacific region, feel free to contact us at Principle.

Want to grow your business in Asia?
Principle is a data-driven marketing agency that grows your business in Japan and the rest of the Asia Pacific market. Click here to learn more about our digital marketing services for the APAC region.